Activity and Activity Coefficient
The activity of a component j, aj, is defined by
|
|
where is the chemical potential of the component j in equilibrium state and
is the chemical potential of this component at its reference state. For example, the activity of component Al in the liquid Al-Mg system referring the Al in Fcc phase is calculated by
|
|
The corresponding Table column name is a(Al@Liquid:Fcc[Al]), or a(Al@Liquid:Fcc).
If a reference state is not specified in Table column name, the default reference state in the database is taken as the reference state. For example, a(Al@Liquid) is calculated by
|
|
Activity coefficient is defined as
|
|
which is available from Table by defining Table column name similar to that of activity. Table column name for the activity coefficient of Al in liquid is r(Al@Liquid:Fcc[Al]), or r(Al@Liquid:Fcc).
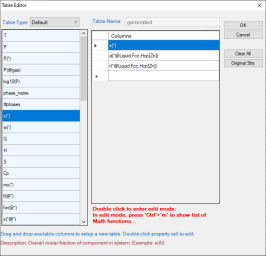
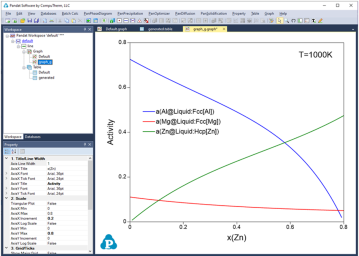
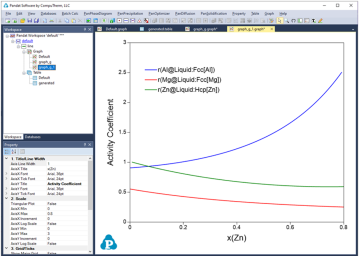
Figure 1 to Figure 4 show the screen images for creating a table of activity and activity coefficient from a line calculation result at 1000K in the Al-Mg-Zn ternary system. The two end points are at x(Mg)=0.2,x(Al)=0.8 and x(Mg)=0.2,x(Zn)=0.8. The liquid phase is the stable phase under this condition. The setting in Figure 1 is to choose Fcc Al, Fcc Mg, and Hcp Zn as the reference state for the activities and activity coefficients.